Intro to SQL Concepts
Learning objective: By the end of this lesson, students will be able to explain the concepts of SQL, specifically focusing on PostgreSQL. Students will understand why these skills are crucial in data management and software development.
What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language), often pronounced “sequel”, is the standard programming language used to manage and manipulate data stored in relational databases. It features a syntax similar to the English language, making it accessible and easy to learn. SQL plays a critical role in data operations, allowing for effective data retrieval, insertion, updating, and deletion.
It’s important to note that while SQL is standardized, its implementation can vary slightly across different Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS). Common RDBMSs like SQLite and PostgreSQL might differ regarding the specific SQL commands they support.
Different types of databases
Databases can be categorized into several types with distinct features and uses. According to DB-Engines Ranking, databases are primarily classified into:
-
Relational databases: Organize data into tables consisting of rows and columns, where each row represents a unique record, and each column represents a field within the record.
-
NoSQL databases: Organize data in a way that does not adhere to the traditional relational database model, and they typically do not use SQL for querying. These databases are designed to provide greater scalability and flexibility with data models, including key-value, document, and graph bases, which are optimized for specific types of data and access patterns.
We’ll use PostgreSQL as our relational database system because it is free and flexible, allowing us to handle data securely and efficiently. It’s also widely supported by a large community, making it reliable and adaptable for scaling our applications.
PostgreSQL and SQL
PostgreSQL is an advanced open-source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) built in 1982 at the University of California, Berkeley. It is known for its robustness, ability to handle large volumes of data, and support for a wide range of SQL functionality.
Relational database structure
Tables, rows, and columns
These are the fundamental structural components of a relational database:
- Tables: A table in a relational database is similar to a spreadsheet. It serves as the primary container for data and is organized into rows and columns.
- Rows: Each row in a table represents a unique instance or record of the entity being stored. For example, each row would represent a single employee in a table of employees.
- Columns: Columns define the specific attributes or fields of the data entity. For example, in a table of employees, you could have columns for employee attributes such as
name,role, andstart_date. Every entry in the same column in a table must conform to the same data type. For example, every entry in thenamecolumn must be a string, and every entry in thestart_datecolumn must be a date.
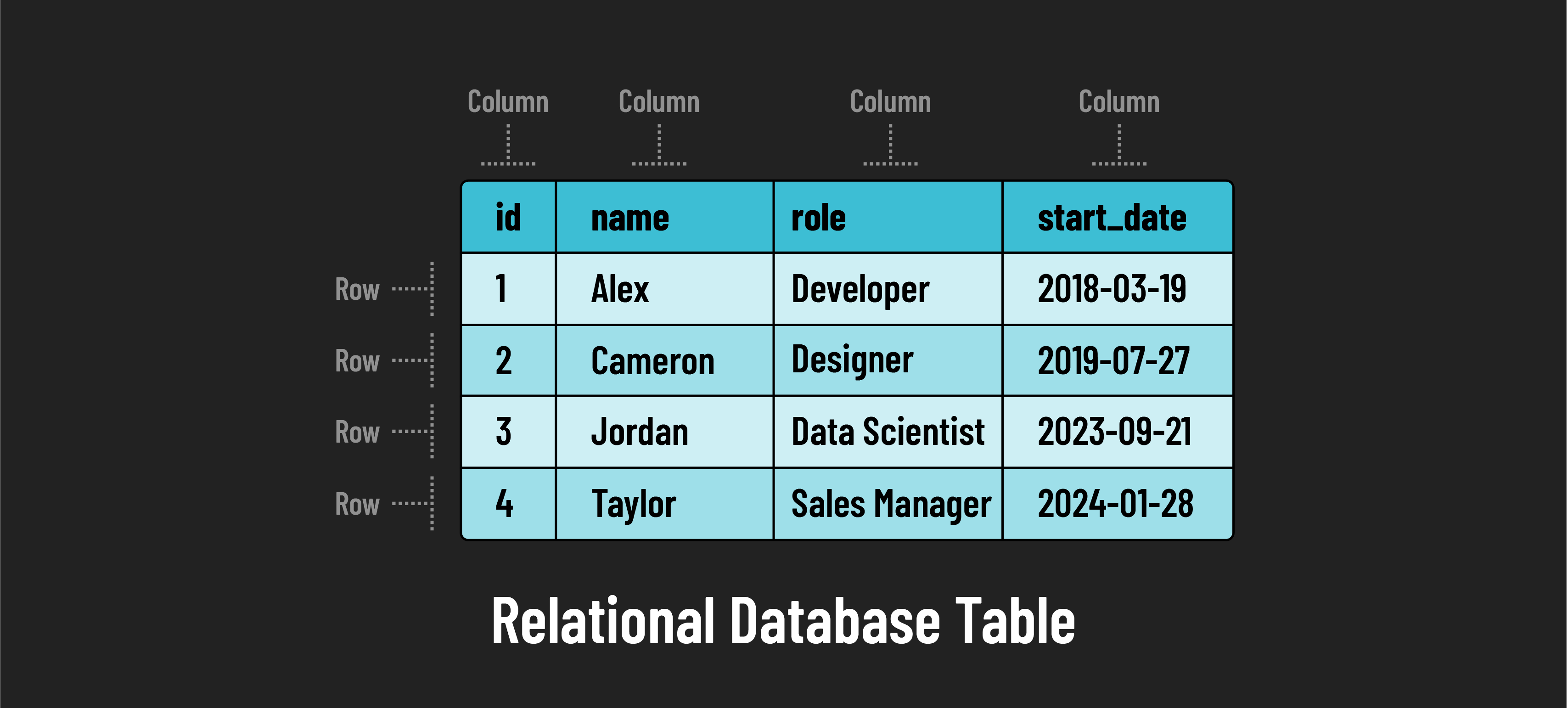
Understanding the relationship between tables, rows, and columns is essential for working with relational databases. These elements work together to store data in an organized and accessible manner, making relational databases a staple in large-scale data management across various industries.