Intro to Express URL Parameters
Learning Objective: By the end of this lesson, students will be able to use URL parameters in Express routes to handle dynamic data in requests.
Understanding URL/Route Parameters
URL Parameters, also known as Route Parameters, are akin to function parameters but within the context of URL paths. They allow dynamic data, like identifiers for specific resources, to be passed through the URL path of an HTTP request.
In simpler terms, it allows us to pass small amounts of information from the browser to the server via the URL.
URL params in Express
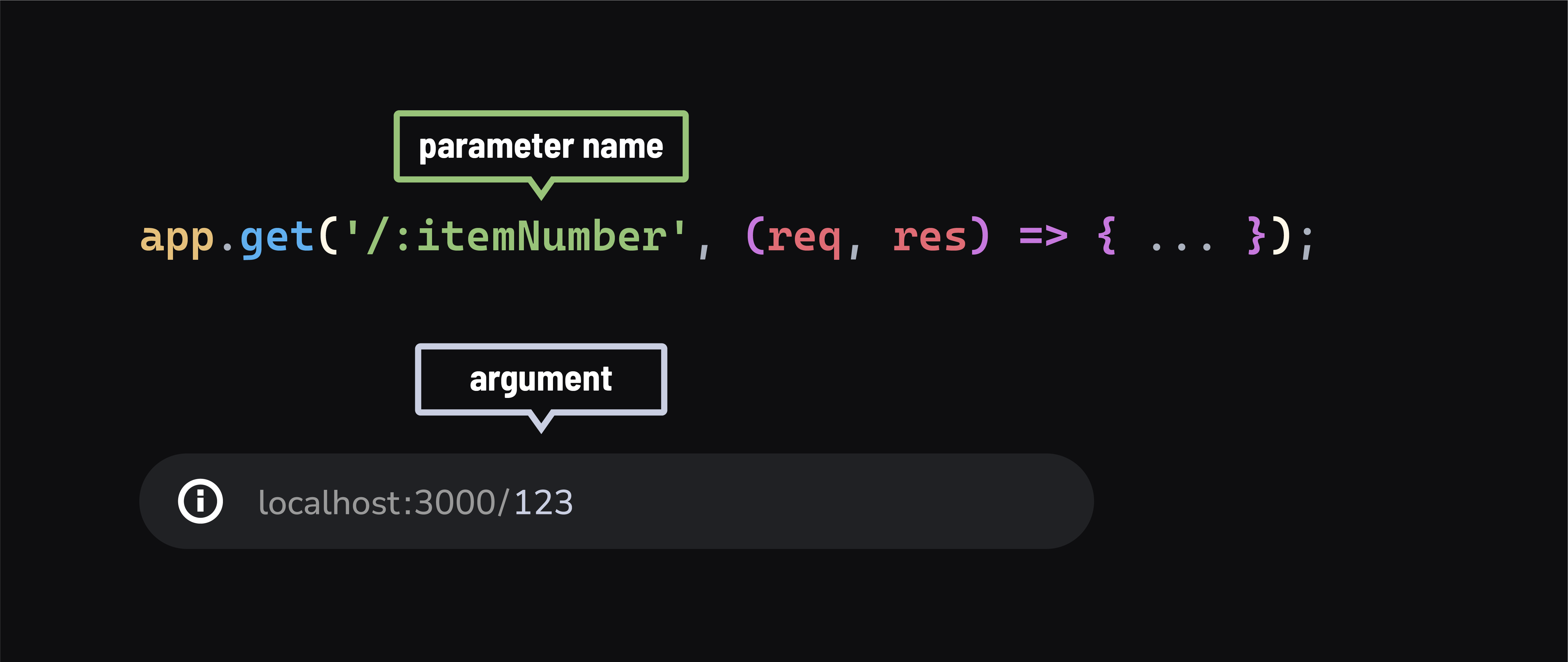
In Express, we define these parameters in the path string, using a colon : followed by the parameter name:
app.get('/:itemNumber', (req, res) => {
// Accessing the parameter
console.log(req.params.itemNumber); // Output could be 123, 456, etc.
// Sending a response with the parameter
res.send(`<h1>Item ${req.params.itemNumber}</h1>`);
});
Just like parameters in JavaScript functions are placeholders for actual values passed during function invocation, URL parameters are placeholders in route definitions. The actual values are provided in the URL when a request is made from the browser.
Testing in the browser
Try visiting localhost:3000/123 and localhost:3000/456 in your browser. Notice how the item number in the console.log and <h1> response changes according to the URL.
How this works:
- The path
/:itemNumberis a template. When a request likelocalhost:3000/123is received, Express maps'123'toitemNumber, which is then accessible viareq.params.itemNumberon the request object.
Example with req.params
- If you
console.log(req.params)in the route above, you’ll get an output like{ itemNumber: '123' }or{ itemNumber: '456' }, depending on the request URL.
Route order and URL parameters
When planning your routes in Express, the order of route definitions is crucial when working with URL parameters
Take a look at the routes below:
app.get('/:name', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Hello ${req.params.name}!`);
});
app.get('/about', (req, res) => {
res.send('About Page');
});
-
In the provided example, the first route
/:nameis dynamic, meaning it uses a route parameter:nameto match any URL path that starts with a/followed by any string. This pattern is quite broad and will match a wide range of URLs, including something like/about. -
The issue arises because this general pattern also matches the specific URL
/about. As a result, a request to/aboutgets intercepted by the first route/:nameinstead of reaching the intended/aboutroute. -
This behavior makes the specific
/aboutroute essentially unreachable, as the server always responds with the first matching route it encounters, which in this case is the more generic/:nameroute. -
To prevent this, it’s important to order routes carefully in Express. More specific routes, like
/about, should be defined before more generic routes, like/:name, to ensure they are correctly matched and accessible.
🎓 You Do
Create a Greeting Route
Practice your new skills:
-
Create a route at
/greet/:name. -
Have it respond with
"Hello, [name]!", replacing[name]with the actual name provided in the URL. -
Test your route by navigating to
localhost:3000/greet/yournamein your browser.
Query Parameters
Another effective way to pass additional information in a URL to a server is through query parameters. Query parameters are added to the end of a URL after a ? and are formatted as key=value pairs. In Express, these parameters are conveniently accessible through the req.query object.
For example, consider the following URL localhost:3000/hello?name=Christy&age=32.
This URL contains two query parameters:
namewith a value of “Christy”agewith a value of “32”.
These parameters follow the ? symbol in the URL and are separated by &.
When a request is made to this URL, the Express server can retrieve these values from the req.query object. The name and age keys in the req.query object correspond to the query parameters in the URL. The server can then use this data, for example, to personalize a response message.
Here’s how the server processes this request in Express:
app.get('/hello', (req, res) => {
// Accessing query parameters from the request
const name = req.query.name;
const age = req.query.age;
// Using the query parameters to customize the response
res.send(`Hello there, ${name}! I hear you are ${age} years old!`);
});
🧠 If we were to
console.logthereq.queryobject, you’ll see an object representation of the query parameters, which in this case would be{ name: "Christy", age: "32" }. This object structure makes it simple to access and use the parameters within the server’s response logic.